Integrate reservoir and fluid data to optimize matrix treatments using acid or nonreactive fluids.
Innovative gas shutoff solution enhances oil production in Caspian offshore field
An operator faced the complex challenge of conducting gas shut off in an openhole gravel-pack (OHGP) completion. The SLB solution combined digital simulation with an optimized pumping strategy for chemical gas shutoff, achieving approximately 68% gas reduction and increased oil productivity. This successful implementation opens opportunities for similar treatments in other complex shutoff wells within the Caspian region and globally.
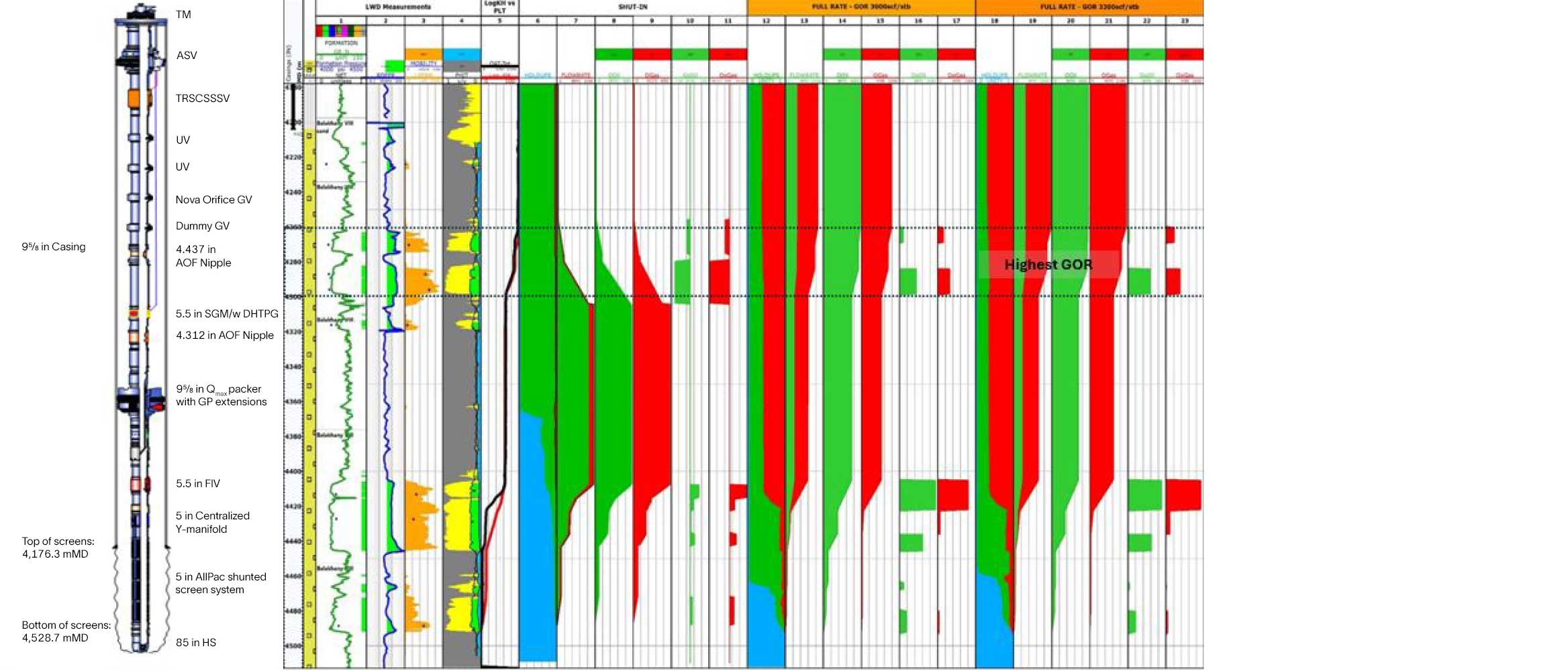
In the vast expanse of the South Caspian region, an international oil and gas operator manages an offshore megastructure, tapping into rich reservoirs beneath the seabed. These reservoirs lie within a multilayered sandstone anticline, where all target formations are weakly consolidated and exhibit low unconfined compressive strength (UCS). To address these challenging geological conditions, the operator adopted the OHGP technique as a proven sand control method. However, as the field matured, new challenges emerged. Gas breakthrough became increasingly common, complicating the operator's efforts to maintain optimal oil production. The once-reliable OHGP method now faced the added burden of managing these gas intrusions, prompting the operator to seek innovative solutions to sustain the field's productivity and tackle the evolving complexities of the aging reservoir.
To address the challenges associated with gas shut off in an OHGP environment, SLB implemented the use of OrganoSEAL R™ rigid organic crosslinked gel system—a polyacrylamide-based gas shutoff (GSO) gel system. The OrganoSEAL R system produces a high-strength crosslinked synthetic polymer gel after activation, which is based on time and temperature settings. This gel is highly effective in treating near-wellbore production problems that require complete blockage. The low molecular weight and lower viscosity of the polymer allow the gel to penetrate the matrix, and its low shear sensitivity ensures stability during placement. A key operational advantage of the OrganoSEAL R system is that it can be jetted out after treatment, rather than requiring drilling out of the wellbore.
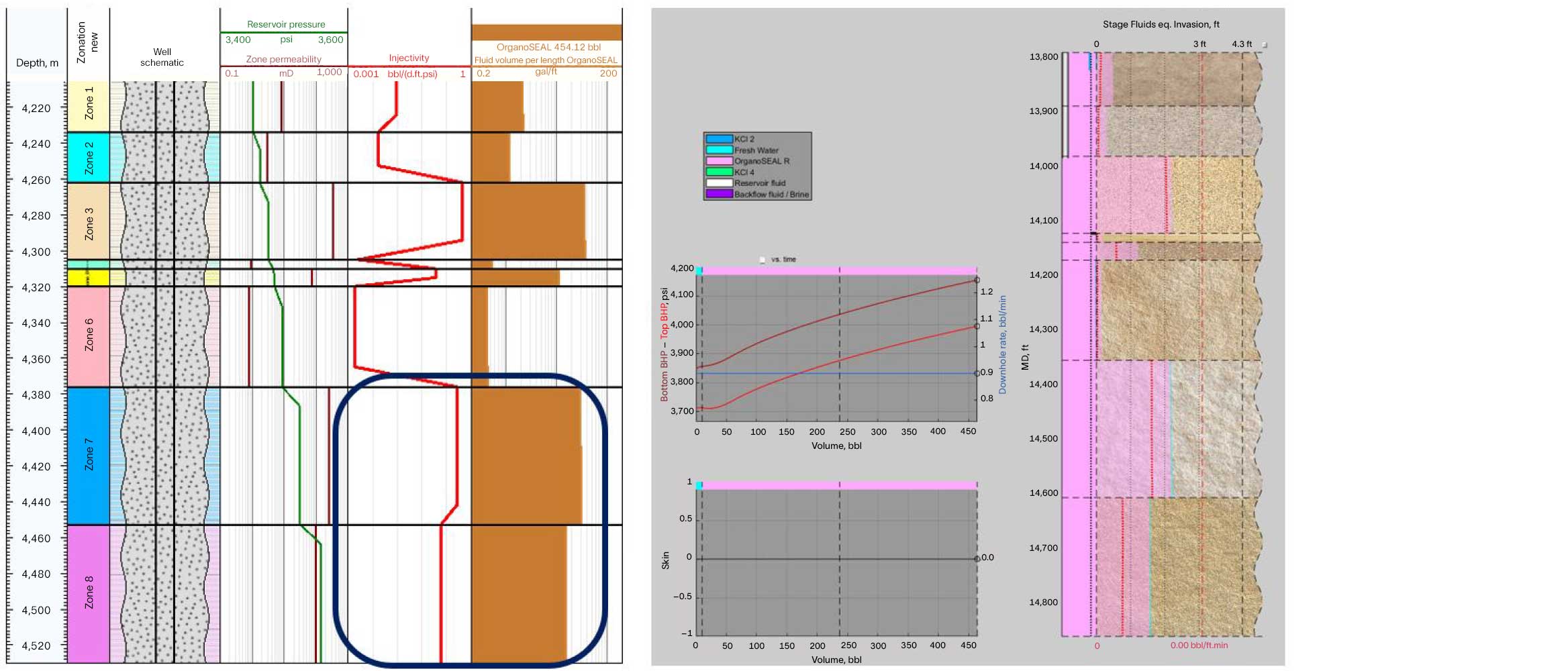
Understanding fluid leakoff paths is essential for developing an effective fluid placement strategy. To comprehend the fluid dynamics and penetration levels into the matrix during the main fluid placement, Kinetix Matrix™ stimulation design software was used. This software helps to calibrate theoretical volumetric requirements and optimize the design, thus reducing the risk of fluid leakoff into the producing zone. By simulating the fluid behavior and adjusting the treatment parameters, the software ensures precise placement and distribution of the GSO gel, minimizing fluid loss and enhancing treatment efficiency.
To further minimize the damage to the underlying producing zones, a highly concentrated viscoelastic surfactant (VES) fluid was chosen. This VES fluid provides a barrier that prevents the GSO gel system from penetrating into the lower zone. Additionally, a heavy concentration of brine (11.2 ppg NaBr) was selected for the VES base brine to enhance its effectiveness. The combination of VES and heavy brine ensures that the GSO gel remains confined to the target zone, preventing unintended shutoff of the producer zone and maintaining productivity. Mechanical temporary zonal isolation was also employed to provide additional assurance that the GSO gel system would not penetrate the lower zone. A retrievable bridge plug was used as a cushion for the VES, creating a temporary barrier between the treated zone and the rest of the wellbore.
The jobs were executed successfully, marking the first chemical shutoff solution for OHGP within the Caspian region. The treatment resulted in a significant increase in oil production and a significant reduction of gas by approximately 68%. The combination of digital solutions to optimize the pumping strategy, along with the use of chemical and mechanical temporary zonal isolation, provided extra assurance for successful placement. This comprehensive approach ensured the effective confinement of the GSO gel to the target zone, preventing any unwanted shut off of the producer zone and maintaining well productivity.
For more information, read SPE-224090-MS.
