Reduce production risk and improve returns.
Nitrogen-free scavenger lowers H2S by 99.7% and enables 63% more gas production
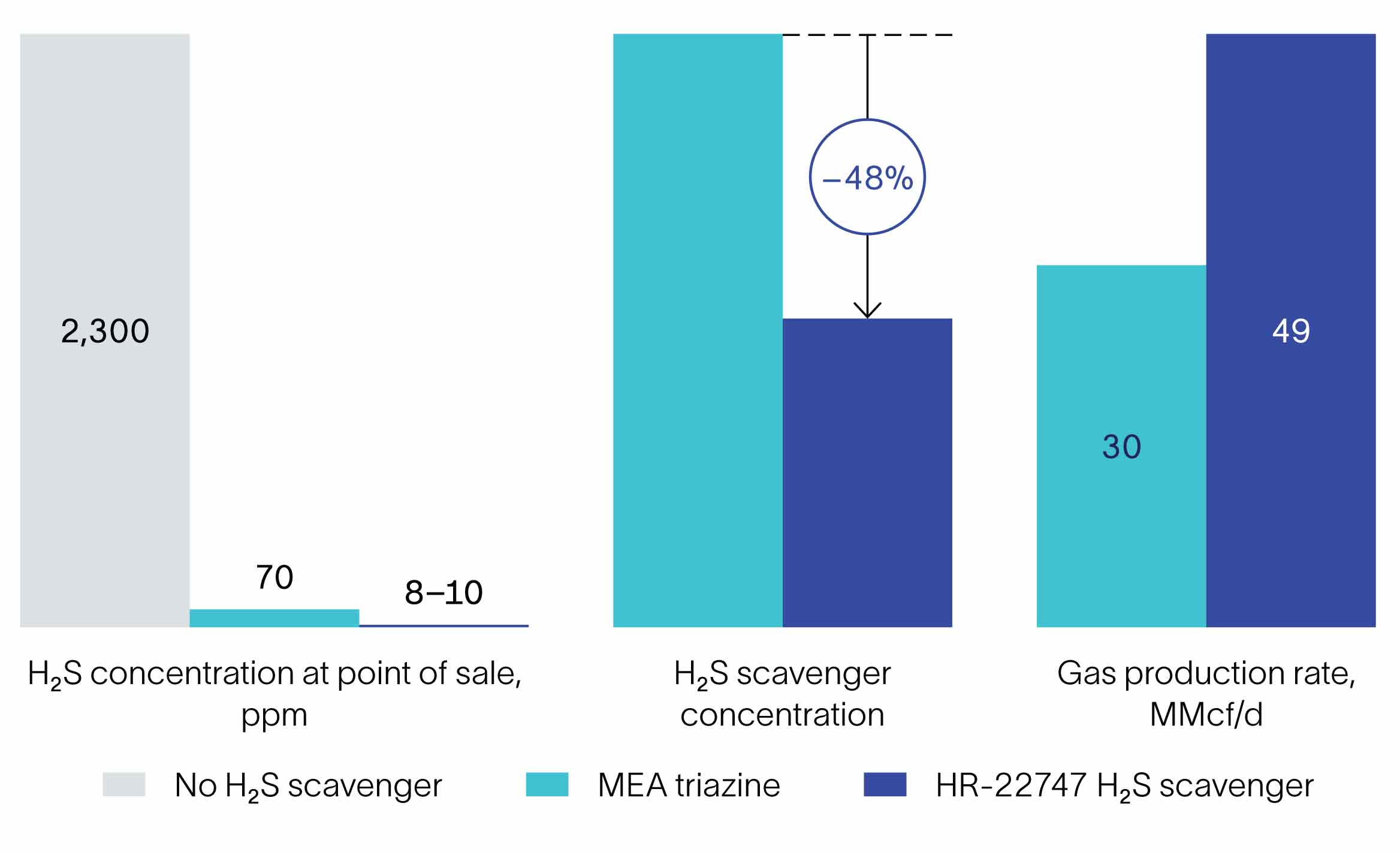
Using an innovative SLB formulation, an operator reduced H2S concentration in natural gas at the point of sale to about one-ninth the level achieved with monoethanolamine (MEA) triazine. The new scavenger was used at nearly 50% lower concentration and also eliminated solids deposition, improving economics.
An operator in the Permian Basin wanted to significantly reduce the 2,300-ppm H2S content in produced gas at the point of sale. The incumbent third-party chemicals provider was using MEA triazine scavenger but could not lower H2S levels below 70 ppm on average. As a result, the operator was facing the risk of having to shut in wells because of pipeline regulations. Some of the challenges to removing H2S were high gas velocities of >100 mi/h [>160 km/h], minimum contact time with the H2S scavenger, few chemical injection points, absence of static mixers and polishing towers, and shifts from bulk to test separators every 24 hours.
SLB proposed using its nitrogen-free H2S scavenger, a clear, colorless, and odorless liquid that reacts instantaneously with H2S and removes it from the gas stream. The first step was a detailed field evaluation, which included
- complete analysis of produced water with different pH levels to determine potential scale tendencies
- determination of CO2 concentration, which could affect injection rate efficiency
- field tests to identify the optimal scavenger injection rate based on the amount of H2S removed.
The operator's facility uses one bulk separator and five test separators to segregate gas, oil, and water from 15 wells; the output gas flows are commingled in a single line before reaching the point of sale. Initially, the operator asked SLB to start replacing the third-party product by injecting the new scavenger into the commingled gas flow, which reduced H2S concentration at the output to 20 ppm from 70 ppm within 30 minutes. After a while, the strategy was extended to each of the six separators in turn, further reducing H2S levels to approximately 14 ppm.
To increase contact time and improve efficiency, the operator subsequently decided to inject the SLB scavenger at the wellheads. The result was an additional reduction in H2S concentration to a consistent 8–10 ppm at the point of sale. The operator was able to increase gas production rates to 49 MMcf/d from about 30 MMcf/d while using approximately 48% lower concentration of scavenger, significantly enhancing profitability. The new product also eliminated other undesirable consequences of using MEA triazine, such as solids deposition and consequent cleanout costs and downtime.