Petrel Advanced Completion Optimization
Using Intersect high-resolution reservoir simulator
Incorporates a workflow for reservoir-centric lower completion design and interval control valve optimization across well life.
The Harash carbonate reservoir, located in Libya's desert, has long posed challenges for oil production due to its complex geology. The C50‑6 well, drilled in 1963 by SOC, was producing from multiple oil‑bearing layers situated above a high‑permeability water zone. Over time, the well's oil production declined significantly as the water/oil contact moved upward, leaving the well producing only 150 bbl/d with a 90% water cut.
SOC's primary objective was to enhance oil production while minimizing water production, thereby improving the well's profitability and operational efficiency. Traditional hydraulic fracturing methods were ineffective due to the lack of a strong barrier between the oil‑producing zone and the water zone below. Previous attempts to address the issue failed to deliver satisfactory results, prompting SOC to seek an innovative solution to isolate the water‑producing zones and optimize oil recovery.
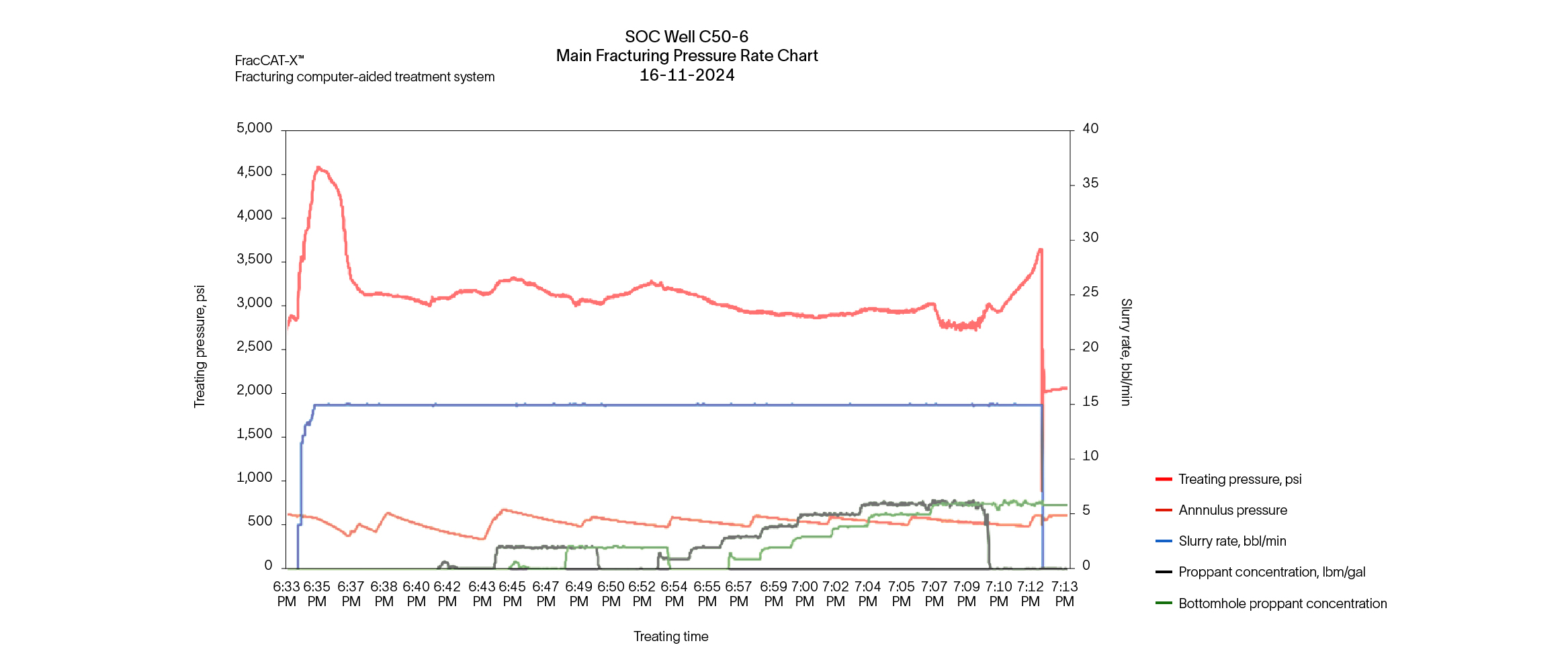
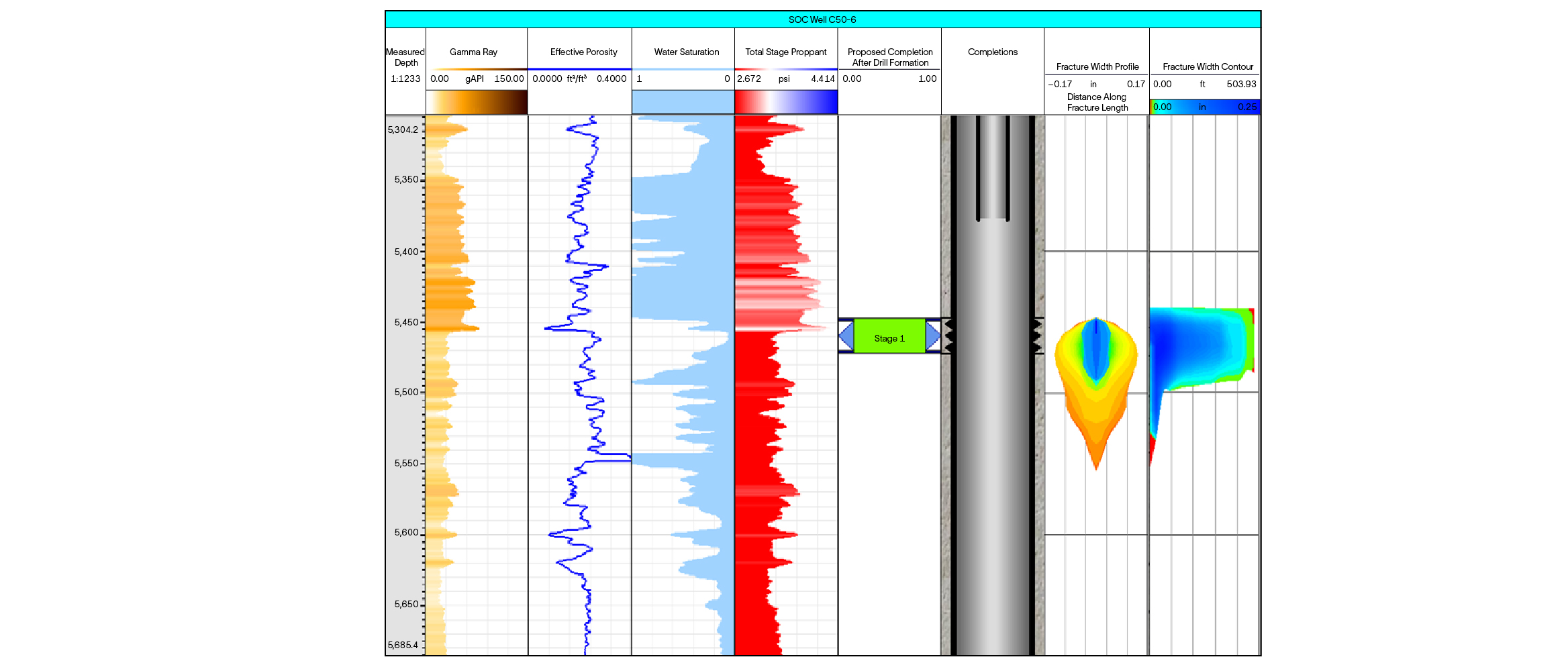
To address the challenges of well C50-6, SLB employed a comprehensive approach, starting with an in-depth analysis of historical openhole logs and recent repeat formation tester (RFT) and production logging tool (PLT) data. Using Kinetix and Petrel software, SLB engineers developed detailed petrophysical and geomechanical models to stimulate hydraulic fracturing scenarios. This analysis highlighted the critical need to prevent fracture breakthrough into the water-producing zone, located approximately 40 ft below the existing perforations.
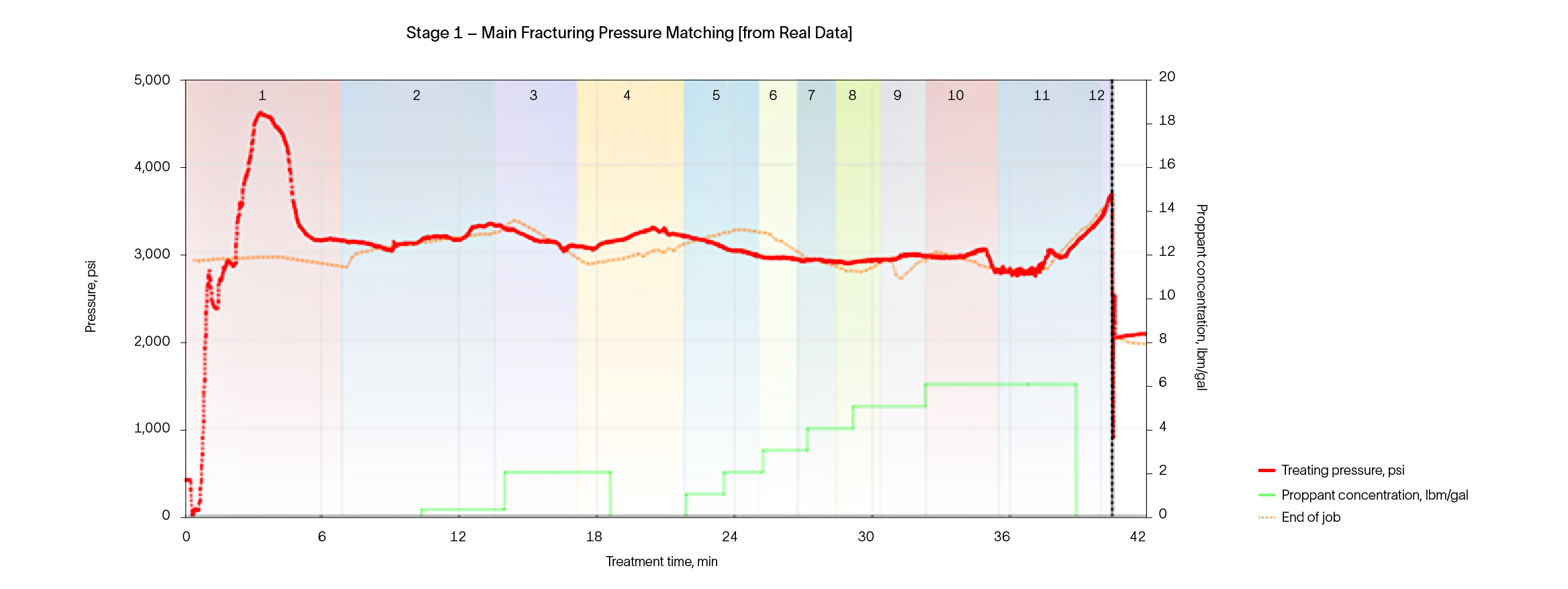
The solution involved isolating the lower perforations and strategically placing new ones based on an optimized design. The fracturing treatment began with two limited-volume DataFRAC fracture data determination service tests using linear gel with FracCON fluid, a relative permeability modifier, and temperature logs to refine the approach. FracCON fluid was used as the pad, followed by the application of BroadBand Shield service diversion technology, which included 6,000 lbm of diverting material to ensure effective fracture containment.
The stimulation treatment also incorporated 45,000 lbm of 16/30 ceramic proppant and 9,000 lbm of RodPROP™ high aspect ratio proppant as to enhance fracture conductivity and oil flow. These targeted interventions transformed the well's production dynamics, increasing output from 150 bbl/d with a 90% water cut to an impressive 1,000 bbl/d with only 2% water cut.
Through the deployment of advanced technologies such as FracCON fluid, BroadBand Shield service, Kinetix and Petrel software, SOC successfully overcame the geological constraints of the Harash carbonate reservoir. This achievement not only revitalized the C50-6 well but also established a predecent for future oil recovery projects in Libya's complex carbonate reservoirs.